Exercise 4.12#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
(a)#
def Power():
print(2**3)
Power()
8
(b)#
def Power2(x,a):
print(x**a)
Power2(3,8)
6561
(c)#
Power2(10,3)
1000
Power2(8,17)
2251799813685248
Power2(131,3)
2248091
(d)#
def Power3(x,a):
result = x**a
return result
(e)#
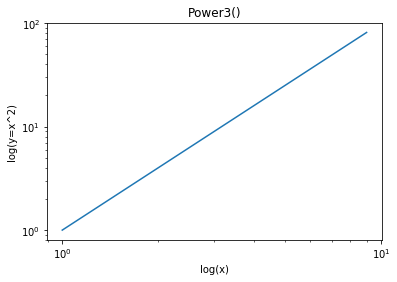
def Plot(log=''):
x = np.arange(1,10)
y = Power3(x,2)
#create plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
#config plot
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y=x^2')
ax.set_title('Power3()')
#change scale according to axis
if log == 'x':
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('log(x)')
if log == 'y':
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_ylabel('log(y=x^2)')
if log == 'xy':
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('log(x)')
ax.set_ylabel('log(y=x^2)')
#draw plot
ax.plot(x, y)
Plot(log='xy')
(f)#
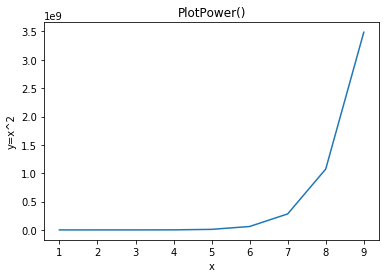
def PlotPower(start,end,power,log=''):
x = np.arange(start,end)
y = np.power(x,end)
#create plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
#config plot
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y=x^2')
ax.set_title('PlotPower()')
#change scale according to axis
if log == 'x':
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('log(x)')
if log == 'y':
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_ylabel('log(y=x^2)')
if log == 'xy':
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('log(x)')
ax.set_ylabel('log(y=x^2)')
#draw plot
ax.plot(x, y)
PlotPower(1,10,3)